The Role of the Mediterranean Diet in Managing Type 2 Diabetes
The Mediterranean diet, characterized by a rich intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, olive oil, and fish, has gained recognition as one of the healthiest dietary patterns. This diet, with its origins in the countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, has proven benefits on cardiovascular health and longevity. More recently, research has begun to highlight its potential role in the prevention and management of Type 2 diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder that has reached epidemic proportions worldwide. In this article, we delve into the impact of the Mediterranean diet on Type 2 diabetes, its potential mechanisms of action, and practical tips for incorporating this dietary pattern into everyday life.

History and Characteristics of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is not a uniform diet but rather a collection of eating habits traditionally practiced by people living in the Mediterranean region. The diet became popularized in the 1960s when Ancel Keys, an American physiologist, conducted the Seven Countries Study. He observed that populations from the Mediterranean region, particularly Southern Italy and Greece, had lower rates of heart disease compared to other Western countries, despite similar fat intake. This finding sparked interest in the Mediterranean diet, leading to numerous studies exploring its health benefits.
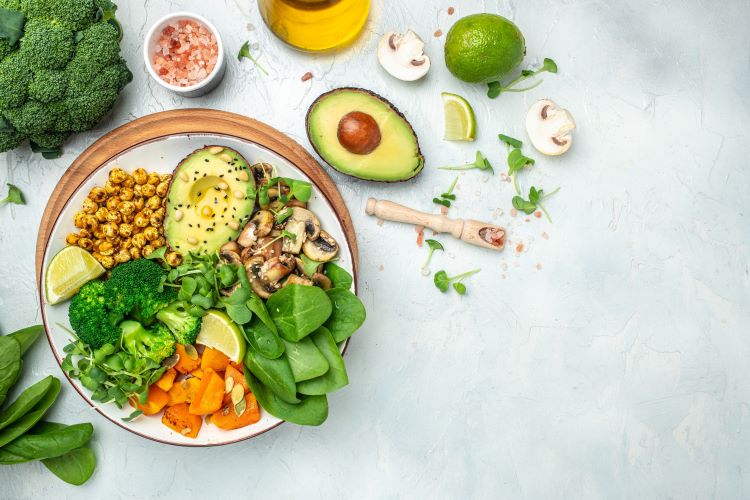
The Mediterranean diet is high in plant-based foods — fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Olive oil is the primary fat source, and fish, poultry, dairy products, and eggs are consumed in moderate amounts. Red meat and sweets are limited. The diet also emphasizes physical activity and enjoying meals with family and friends, reflecting the Mediterranean lifestyle.
The Mediterranean Diet and Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is primarily characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Chronic high blood glucose can cause complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
Several studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet can help prevent and manage Type 2 diabetes. A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies found that strict adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 23% reduced risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, clinical trials have shown that a Mediterranean diet can improve glycemic control in individuals already diagnosed with diabetes.
How Does the Mediterranean Diet Benefit People with Diabetes?
The beneficial effects of the Mediterranean diet on diabetes are likely due to its high content of dietary fiber and healthy fats. Dietary fiber can slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood glucose and insulin levels. Moreover, monounsaturated fats found in olive oil and nuts can improve insulin sensitivity.
Additionally, the Mediterranean diet has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are involved in the development of insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. Therefore, a diet rich in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds can help manage these conditions.
Incorporating the Mediterranean Diet into Daily Life
Adopting a Mediterranean diet does not require drastic changes. Here are some practical tips:
-
Replace butter with olive oil in cooking and salad dressings.
-
Choose whole grains instead of refined grains.
-
Increase vegetable intake by adding them to every meal.
-
Consume at least two servings of fish per week.
-
Opt for poultry, fish, or plant-based proteins instead of red meat.
-
Enjoy fruit for dessert instead of sweets.
Remember, physical activity is an essential part of the Mediterranean lifestyle. Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and improve insulin sensitivity, further aiding diabetes management.
Conclusion
The Mediterranean diet, with its emphasis on plant-based foods and healthy fats, can play a significant role in the prevention and management of Type 2 diabetes. While more research is necessary to understand fully the diet’s potential mechanisms of action, it’s clear that adopting a Mediterranean dietary pattern can be a beneficial strategy for individuals at risk for or already diagnosed with diabetes. As always, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle.