All About Prefabricated Buildings
Prefabricated buildings represent a revolutionary approach to construction that combines efficiency, quality control, and design flexibility. These structures are manufactured off-site in controlled factory environments before being transported and assembled at their final location. From residential homes to commercial spaces, prefabricated construction offers numerous advantages including reduced build times, consistent quality standards, and often more predictable costs compared to traditional site-built construction methods.
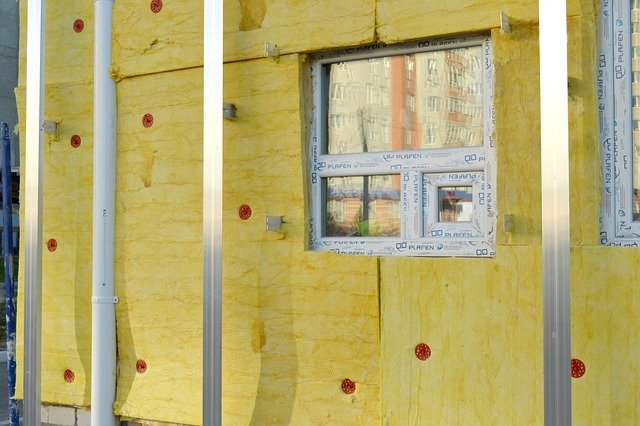

Prefabricated construction has transformed the building industry by offering a systematic approach to creating structures that meet modern demands for efficiency and quality. This construction method involves manufacturing building components or entire sections in controlled factory settings, then transporting them to the construction site for assembly. The process allows for greater precision, reduced waste, and faster project completion times.
What Makes High-Quality Prefabs Stand Out
High-quality prefabs distinguish themselves through superior materials, advanced manufacturing processes, and rigorous quality control standards. Factory-controlled environments eliminate weather-related delays and inconsistencies that often plague traditional construction. Quality prefabricated buildings utilize engineered lumber, steel framing, and advanced insulation systems that often exceed conventional building standards. The precision manufacturing process ensures tight tolerances, better energy efficiency, and structural integrity that can surpass site-built alternatives.
Manufacturers of premium prefabricated buildings typically employ computer-aided design and automated cutting systems to ensure accuracy. These facilities maintain consistent temperature and humidity levels, allowing materials to cure properly and joints to fit precisely. Quality control inspectors examine each component before it leaves the factory, identifying and correcting issues that might otherwise go unnoticed on a traditional construction site.
Modern Prefab Solutions for Contemporary Needs
Modern prefab solutions address diverse architectural and functional requirements across residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Today’s prefabricated buildings can accommodate complex designs, multi-story structures, and specialized uses such as healthcare facilities, educational buildings, and retail spaces. Advanced engineering allows for large open spaces, custom floor plans, and integration of modern building systems including smart home technology and renewable energy components.
Contemporary prefabricated construction methods include modular construction, where complete rooms or sections are built off-site, and panelized systems that create walls, floors, and roof components separately. Hybrid approaches combine both methods to optimize efficiency and design flexibility. These solutions can incorporate sustainable materials, energy-efficient systems, and modern aesthetics that rival any traditionally constructed building.
Innovative Prefab Design Trends and Technologies
Innovative prefab design continues to push boundaries in both aesthetics and functionality. Architects and manufacturers now collaborate to create buildings that challenge traditional perceptions of prefabricated construction. Modern designs incorporate large windows, open floor plans, and contemporary finishes that create spaces indistinguishable from custom-built structures.
Technological advances include Building Information Modeling (BIM) software that allows precise planning and coordination between design and manufacturing phases. Three-dimensional modeling helps identify potential issues before production begins, reducing errors and ensuring seamless assembly. Some manufacturers now use robotics and automated systems to improve precision and reduce production time.
Construction Process and Timeline Benefits
The prefabricated construction process typically begins with design development and engineering, followed by factory production while site preparation occurs simultaneously. This parallel approach significantly reduces overall project timelines compared to sequential traditional construction methods. Most prefabricated buildings can be manufactured in four to twelve weeks, depending on complexity and size.
Site preparation for prefabricated buildings often requires less time since foundation requirements may be simpler and utility connections are pre-planned. Assembly typically takes days or weeks rather than months, minimizing weather exposure and site disruption. The controlled manufacturing environment also reduces material waste and allows for better inventory management.
Cost Analysis and Provider Comparison
Prefabricated building costs vary significantly based on size, complexity, location, and manufacturer. Understanding pricing structures helps buyers make informed decisions about their construction projects.
| Provider Type | Cost Range (per sq ft) | Typical Features |
|---|---|---|
| Budget Manufacturers | $80-$120 | Basic finishes, standard layouts, limited customization |
| Mid-Range Providers | $120-$180 | Quality materials, moderate customization, energy-efficient options |
| Premium Manufacturers | $180-$300+ | Custom designs, high-end finishes, advanced building systems |
| Luxury/Architectural | $300-$500+ | Architect-designed, premium materials, cutting-edge technology |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Additional costs include site preparation, foundation work, utility connections, and local permits. Transportation costs depend on distance from manufacturing facility to building site. Some manufacturers offer turnkey services including site work and assembly, while others provide building packages requiring local contractors for completion.
Quality Standards and Building Codes
Prefabricated buildings must meet the same building codes and standards as traditional construction. Many manufacturers exceed minimum requirements to ensure structural integrity and longevity. Quality prefabricated buildings often achieve superior energy efficiency ratings and may qualify for green building certifications.
Building inspections occur both at the manufacturing facility and at the construction site. Factory inspections ensure components meet specifications before shipment, while site inspections verify proper assembly and compliance with local codes. This dual inspection process often results in higher quality control than traditional construction methods.
Prefabricated construction represents a mature and sophisticated approach to building that offers numerous advantages over traditional methods. From faster construction timelines and improved quality control to design flexibility and cost predictability, prefabricated buildings continue to gain acceptance across various market segments. As technology advances and manufacturing processes improve, prefabricated construction will likely play an increasingly important role in meeting growing demands for efficient, sustainable, and high-quality buildings.